Uninterruptable Power Supply: A Complete Guide to Reliable Power Protection
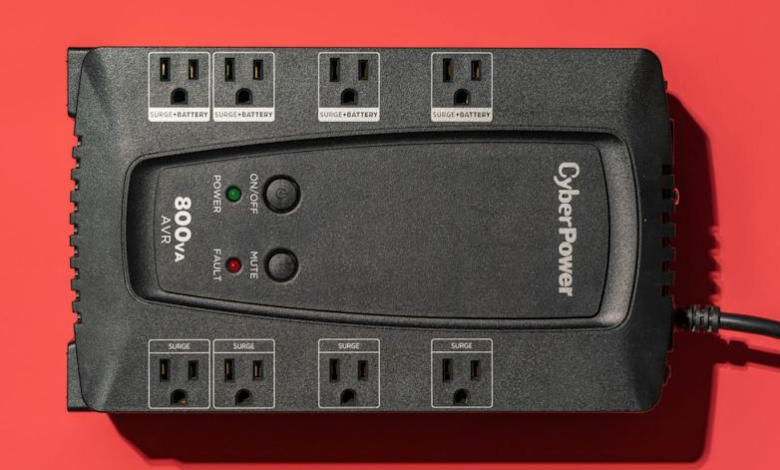

In today’s technology-driven world, continuous and stable power is essential for homes, offices, data centers, healthcare facilities, and industrial operations. Power outages, voltage fluctuations, and electrical disturbances can cause data loss, equipment damage, and costly downtime. This is where an uninterruptable power supply plays a critical role. An uninterruptable power supply, commonly known as a UPS, provides instant backup power and protects connected devices from electrical irregularities.
This article explores the concept, working principles, types, benefits, applications, and maintenance of an uninterruptable power supply, helping you understand why it is a vital component of modern power management.
What Is an Uninterruptable Power Supply?
An uninterruptable power supply is an electrical device that provides emergency power to connected equipment when the main power source fails. Unlike generators, which require time to start, a UPS delivers power instantly using stored energy from batteries or capacitors. This immediate response ensures that critical systems remain operational without interruption.
In addition to backup power, an uninterruptable power supply also conditions incoming electricity by regulating voltage, filtering noise, and protecting against surges and spikes. This dual function makes it essential for safeguarding sensitive electronic equipment.
See also: Vazouagora18 Best Real Estate Investment Strategies
How an Uninterruptable Power Supply Works
The basic operation of an uninterruptable power supply involves three main components: a rectifier, a battery system, and an inverter. Under normal conditions, the rectifier converts incoming AC power into DC power to charge the batteries. When a power failure or disturbance occurs, the inverter instantly converts the stored DC power back into AC power to supply connected devices.
The transition from mains power to battery power happens so quickly that connected equipment continues operating without shutdown. This seamless transfer is what differentiates an uninterruptable power supply from conventional backup solutions.
Types of Uninterruptable Power Supply Systems
There are several types of uninterruptable power supply systems, each designed for different levels of protection and applications.
Standby Uninterruptable Power Supply
A standby uninterruptable power supply is the most basic and cost-effective option. It remains idle during normal operation and switches to battery power when a power outage is detected. This type is commonly used for personal computers, home offices, and small electronic devices.
Line-Interactive Uninterruptable Power Supply
A line-interactive uninterruptable power supply offers improved voltage regulation compared to standby models. It can correct minor voltage fluctuations without switching to battery power, extending battery life. This type is ideal for small businesses, network equipment, and workstations.
Online Uninterruptable Power Supply
An online uninterruptable power supply provides the highest level of protection. It continuously powers connected devices through the inverter, completely isolating them from incoming power issues. This type is widely used in data centers, hospitals, and industrial environments where uninterrupted power is critical.
Key Benefits of Using an Uninterruptable Power Supply
An uninterruptable power supply offers multiple advantages that go beyond simple backup power.
One of the most important benefits is data protection. Sudden power loss can corrupt files, damage operating systems, and disrupt ongoing processes. A UPS allows sufficient time to save data and shut down systems safely.
Another major benefit is equipment protection. Electrical surges, voltage spikes, and power fluctuations can shorten the lifespan of electronic devices. An uninterruptable power supply filters and stabilizes power, preventing long-term damage.
Operational continuity is another significant advantage. For businesses, even a brief power interruption can lead to financial losses and reduced productivity. A UPS ensures continuous operation during short outages and provides time to activate alternative power sources.
Applications of Uninterruptable Power Supply Systems
Uninterruptable power supply systems are used across a wide range of industries and environments.
In home settings, a UPS protects computers, routers, and smart devices from power disruptions. In offices, it ensures uninterrupted operation of workstations, servers, and communication systems.
Data centers rely heavily on uninterruptable power supply systems to maintain uptime and protect critical infrastructure. Healthcare facilities use UPS systems to ensure that life-saving equipment continues functioning during power failures.
Industrial applications also benefit from uninterruptable power supply systems by preventing production downtime and protecting automation systems from electrical disturbances.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Uninterruptable Power Supply
Selecting the right uninterruptable power supply requires careful evaluation of several factors.
Power capacity is one of the most important considerations. The UPS must be capable of handling the total load of connected equipment. Runtime requirements are also crucial, as they determine how long the UPS can provide power during an outage.
Battery type and lifespan should be evaluated to ensure long-term reliability. Additionally, features such as voltage regulation, monitoring capabilities, and scalability can influence the overall effectiveness of an uninterruptable power supply.
Environmental conditions, including temperature and space availability, should also be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Maintenance and Best Practices for Uninterruptable Power Supply
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure that an uninterruptable power supply performs reliably when needed. Regular battery inspections and timely replacements are critical, as batteries degrade over time.
Routine testing helps verify that the UPS can handle load requirements during an outage. Keeping the system clean, ensuring proper ventilation, and monitoring performance indicators contribute to long-term reliability.
It is also important to follow manufacturer guidelines and schedule professional servicing when necessary to maintain optimal performance.
FAQs About Uninterruptable Power Supply
What is the main purpose of an uninterruptable power supply?
The main purpose of an uninterruptable power supply is to provide instant backup power and protect electronic equipment from power outages and electrical disturbances.
How long can an uninterruptable power supply provide power?
The runtime of an uninterruptable power supply depends on battery capacity and load size. It can range from a few minutes to several hours with additional battery support.
Is an uninterruptable power supply the same as a generator?
No, an uninterruptable power supply provides immediate power with no delay, while a generator requires time to start and typically supports longer outages.
Can an uninterruptable power supply protect against voltage fluctuations?
Yes, an uninterruptable power supply regulates voltage and filters electrical noise, protecting equipment from surges, spikes, and fluctuations.
How often should UPS batteries be replaced?
UPS batteries typically need replacement every three to five years, depending on usage, environment, and battery type.
Conclusion
An uninterruptable power supply is an essential solution for ensuring continuous power, protecting sensitive equipment, and maintaining operational stability. From homes and offices to data centers and healthcare facilities, the importance of reliable power cannot be overstated. By understanding how an uninterruptable power supply works, the different types available, and best practices for selection and maintenance, users can make informed decisions that safeguard both data and equipment. Investing in the right uninterruptable power supply is not just a precaution—it is a critical step toward uninterrupted productivity and long-term reliability.